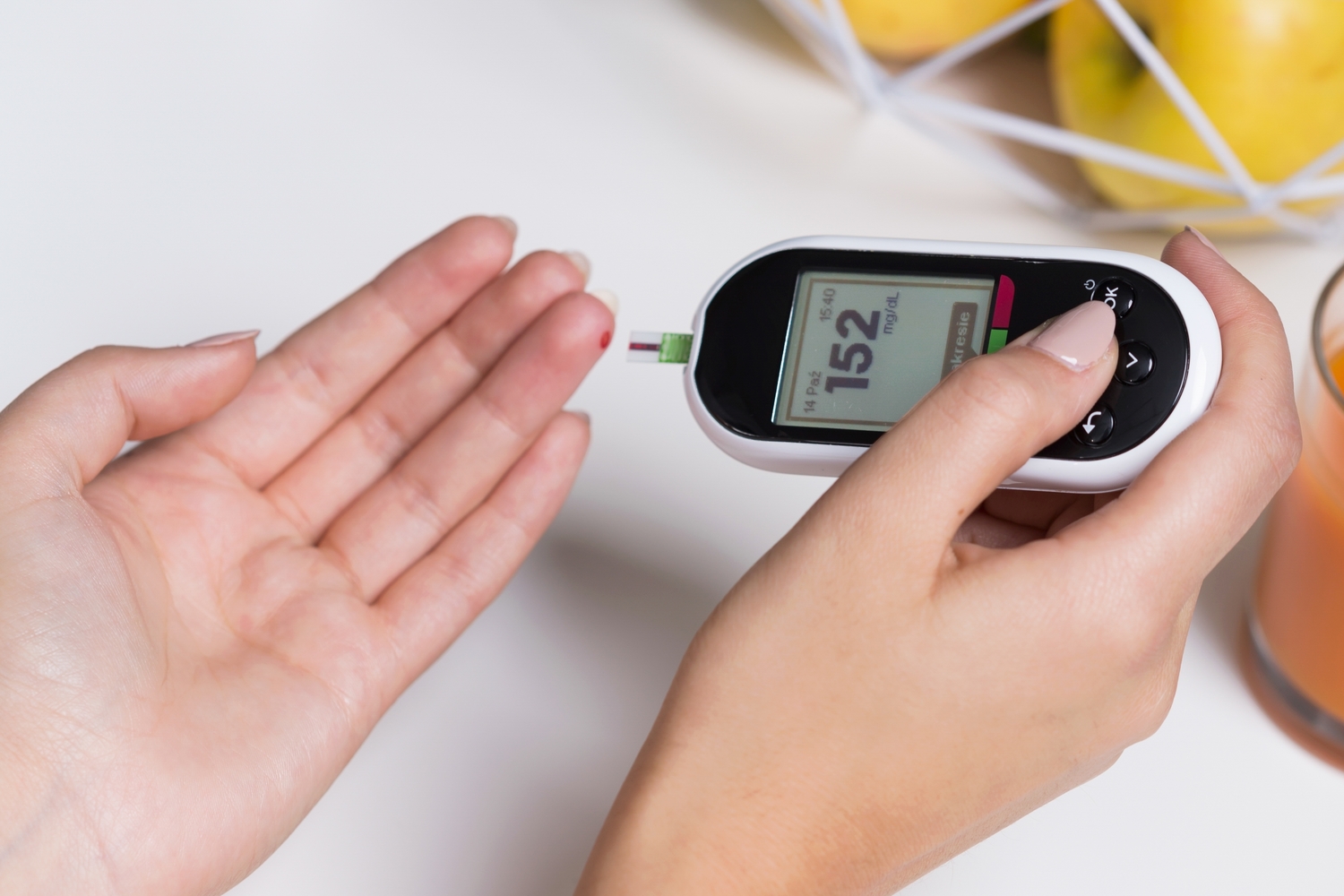
Diabetes and its types
The body breaks down the carbohydrates in the food into smaller elements called glucose. Glucose is used by the cells to produce the required energy for normal functioning of various organs and for providing the energy for the day-to-day activities. For glucose to be utilized by the cells, a hormone called insulin is required, which is produced by the pancreas.
When the body does not produce enough insulin or cannot utilize the insulin produced, it leads to a condition called diabetes. It results in increased glucose levels in the blood, which could be harmful to the blood vessels and various organs. It is an irreversible disorder, but one can lead a healthy life by keeping a constant check on the blood sugar levels.
Types of diabetes
There are three types of the condition: type 1, type 2, and gestational:
- Type 1 diabetes
Also called insulin-dependent diabetes, type-1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition. In this case, the body’s immune system attacks the pancreatic cells that produce insulin, leaving the body with no insulin. It usually occurs during childhood, which is why it is called juvenile diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes could be due to genetic inheritance or due to faulty beta cells of the pancreas, which are responsible for the production of insulin. Type 1 diabetes poses various health risks in the long run. The blood vessels supplying blood to organs like the eyes, kidneys, and nerves become weak or damaged, giving rise to diseases related to those organs. Heart disease and stroke are some of the serious complications that can arise out of this type. - Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes affects over 26 million American adults. Up to 95% of cases of diabetes are those of type 2. Unlike type 1, the pancreas is able to produce insulin in type 2, but the quantity is not sufficient. In some cases, the cells might become resistant to insulin, which is termed as insulin resistance. In both these cases, the glucose levels become high and cause damage to the tiny blood vessels or capillaries.
Though not as harmful as type 1 diabetes, type 2 also poses the risk of heart disease and stroke. People who are obese are at a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Obese people have insulin resistance, because of which no amount of insulin produced helps in reducing the levels of glucose in the blood. - Gestational diabetes
Diabetes triggered during pregnancy is termed as gestational diabetes. It is usually triggered in the second or the third trimester due to temporary insulin resistance. It is of utmost importance to keep the blood sugar levels under check during pregnancy since high sugar levels in the mother could impact the growth and development of the fetus. Gestational diabetes is resolved after pregnancy, but a woman with gestational diabetes is at a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes at later stages of life.


